Diseases Caused by Viruses: An Overview for Competitive Exam Aspirants
Viruses are microscopic organisms responsible for a wide range of diseases affecting humans, animals, and even plants. For students preparing for competitive exams like UPSC, SSC, or state-level tests in India, having a thorough understanding of viral diseases is essential. This blog will provide an overview of major viral diseases, their symptoms, transmission, and prevention, with a focus on topics relevant for Indian exams.
Here is the list of diseases caused by viruses:
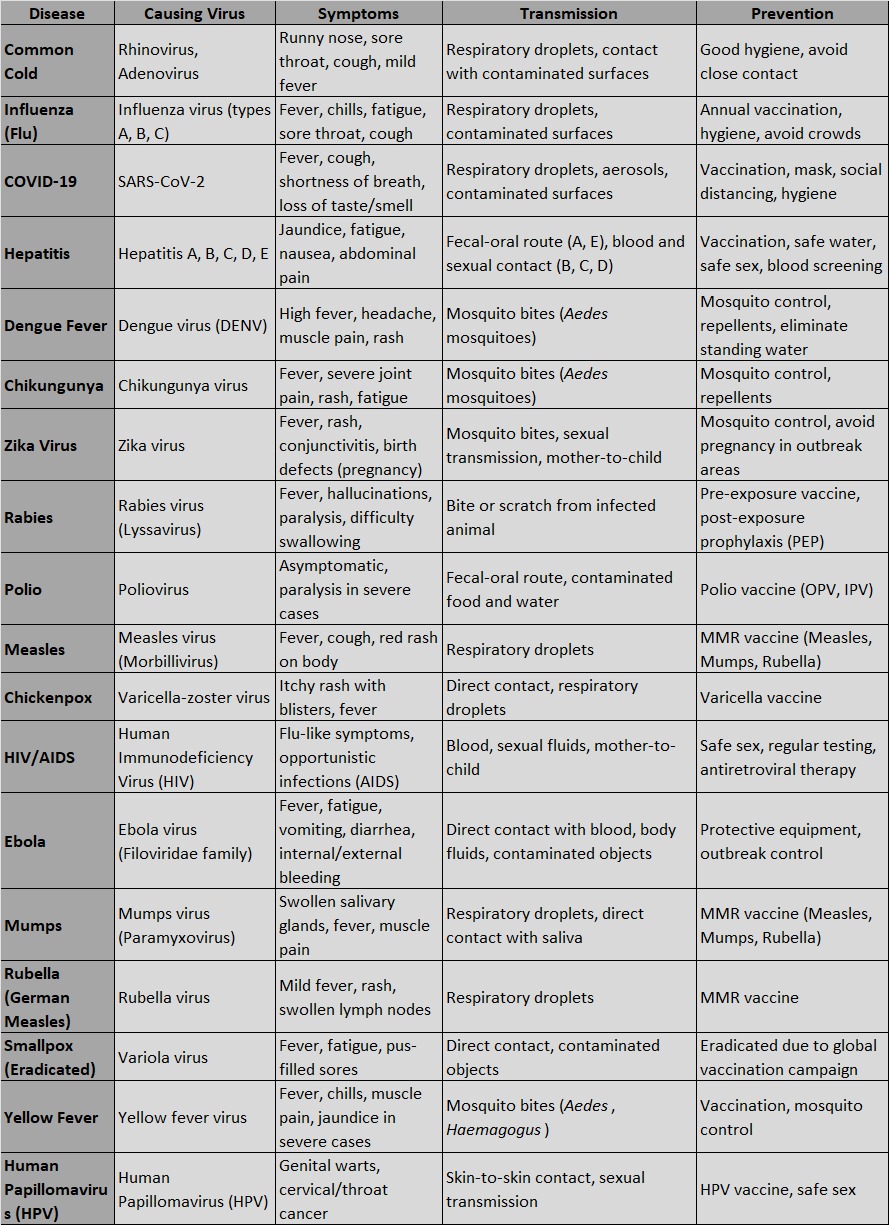
1. Common Cold
- Causing Virus: Rhinovirus, Adenovirus
- Symptoms: Runny nose, sore throat, cough, congestion, mild fever, and body aches.
- Transmission: Spread through droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, and through contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Prevention: Maintaining good hygiene, washing hands, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
2. Influenza (Flu)
- Causing Virus: Influenza virus (types A, B, and C)
- Symptoms: High fever, chills, muscle pain, fatigue, sore throat, runny nose, and cough.
- Transmission: Primarily spread via respiratory droplets and contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Prevention: Annual vaccination, good hygiene, avoiding crowded places during outbreaks.
3. COVID-19
- Causing Virus: SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2)
- Symptoms: Fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, loss of taste or smell, and in severe cases, respiratory distress.
- Transmission: Spread through respiratory droplets, aerosols, and contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Prevention: Vaccination, wearing masks, maintaining social distance, hand hygiene.
4. Hepatitis
- Causing Viruses: Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viruses
- Symptoms: Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Transmission:
- Hepatitis A and E: Fecal-oral route, contaminated food and water.
- Hepatitis B, C, and D: Blood, sexual contact, and from mother to child during birth.
- Prevention: Vaccination (for Hepatitis A and B), safe drinking water, proper sanitation, and safe blood transfusions.
5. Dengue Fever
- Causing Virus: Dengue virus (DENV), transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.
- Symptoms: High fever, severe headache, joint and muscle pain, rash, and bleeding tendencies in severe cases.
- Transmission: Mosquito bites from an infected Aedes species.
- Prevention: Avoiding mosquito bites by using repellents, mosquito nets, and eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed.
6. Chikungunya
- Causing Virus: Chikungunya virus, transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes.
- Symptoms: Sudden onset of fever, severe joint pain, muscle pain, rash, and fatigue.
- Transmission: Spread by mosquito bites.
- Prevention: Similar to dengue prevention, involving mosquito control and avoiding bites.
7. Zika Virus
- Causing Virus: Zika virus, transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.
- Symptoms: Mild fever, rash, conjunctivitis, muscle pain, and headache. Zika can cause birth defects if a pregnant woman is infected.
- Transmission: Mosquito bites, sexual transmission, and from mother to fetus.
- Prevention: Avoiding mosquito bites, especially for pregnant women.
8. Rabies
- Causing Virus: Rabies virus (a type of Lyssavirus)
- Symptoms: Initial symptoms include fever, headache, and weakness. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include hallucinations, paralysis, and difficulty swallowing. Rabies is almost always fatal once symptoms appear.
- Transmission: Spread through the bite or scratch of an infected animal, typically dogs.
- Prevention: Pre-exposure vaccination for high-risk individuals and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) after exposure.
9. Polio
- Causing Virus: Poliovirus
- Symptoms: Most people show no symptoms, but in severe cases, it can lead to paralysis, difficulty breathing, and death.
- Transmission: Fecal-oral route, contaminated food, water, or direct contact with infected individuals.
- Prevention: Oral polio vaccine (OPV) and inactivated polio vaccine (IPV).
10. Measles
- Causing Virus: Measles virus (a type of Morbillivirus)
- Symptoms: High fever, cough, runny nose, inflamed eyes, and a characteristic red rash that starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body.
- Transmission: Highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets.
- Prevention: Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccine.
11. Chickenpox
- Causing Virus: Varicella-zoster virus
- Symptoms: Itchy rash with blisters, fever, and tiredness.
- Transmission: Spread through direct contact with the rash or through the air by coughing and sneezing.
- Prevention: Vaccination (Varicella vaccine).
12. HIV/AIDS
- Causing Virus: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- Symptoms: Initial flu-like symptoms, followed by a long asymptomatic phase. Over time, it weakens the immune system, leading to opportunistic infections and diseases (AIDS).
- Transmission: Spread through contact with infected blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
- Prevention: Safe sex practices, regular HIV testing, use of antiretroviral therapy (ART), and avoiding needle sharing.
13. Ebola
- Causing Virus: Ebola virus (part of the Filoviridae family)
- Symptoms: Sudden onset of fever, fatigue, muscle pain, followed by vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and in severe cases, internal and external bleeding.
- Transmission: Direct contact with blood, body fluids, and tissues of infected individuals or animals.
- Prevention: Avoiding contact with infected individuals, proper use of protective equipment in healthcare settings, and controlling outbreaks through quarantine and proper burial practices.
14. Mumps
- Causing Virus: Mumps virus (a member of the Paramyxovirus family)
- Symptoms: Swollen salivary glands, fever, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. In severe cases, it can lead to meningitis, encephalitis, or hearing loss.
- Transmission: Spread through respiratory droplets or direct contact with an infected person’s saliva.
- Prevention: Mumps, Measles, and Rubella (MMR) vaccine.
15. Rubella (German Measles)
- Causing Virus: Rubella virus
- Symptoms: Mild fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes. In pregnant women, rubella can cause serious birth defects.
- Transmission: Spread through respiratory droplets.
- Prevention: Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccine.
16. Smallpox (Eradicated)
- Causing Virus: Variola virus
- Symptoms: High fever, fatigue, and a distinctive rash that turns into pus-filled sores.
- Transmission: Spread through direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects.
- Prevention: Smallpox was eradicated globally in 1980 due to a successful vaccination campaign, making it the first disease eradicated by humans.
17. Yellow Fever
- Causing Virus: Yellow fever virus, transmitted by Aedes and Haemagogus mosquitoes.
- Symptoms: Fever, chills, muscle pain, nausea, and in severe cases, jaundice, bleeding, and organ failure.
- Transmission: Spread through mosquito bites.
- Prevention: Vaccination, mosquito control, and avoiding mosquito-prone areas.
18. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- Causing Virus: Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- Symptoms: Many strains are asymptomatic, but some can cause genital warts, cervical, throat, and other cancers.
- Transmission: Spread through skin-to-skin contact, primarily during sexual activity.
- Prevention: HPV vaccine, safe sexual practices, and regular screening for cervical cancer.
Importance of Understanding Viral Diseases for Competitive Exams
For competitive exams like the Civil Services, SSC, and state-level exams, the above list of Diseases caused by viruses is frequently included in sections on General Science, Public Health, and Current Affairs. Candidates may be asked about:
- Types of viruses and their characteristics
- Modes of transmission
- Prevention and control measures
- Global and national initiatives to combat viral diseases (e.g., vaccination campaigns, eradication efforts)
The above list of diseases caused by viruses is essential for acing these exams but also crucial for promoting public health awareness. Recent events, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, have highlighted the importance of understanding virology and epidemiology.
Previous Post: Diseases Caused by Bacteria
[…] Previous Post: Diseases Caused by Virus […]
[…] Viral Diseases: These are caused by viruses. Some common examples include SARS, COVID-19, and the flu. Viruses spread quickly through close contact with infected individuals, respiratory droplets, or contaminated surfaces. […]